How many volts are there in a battery? If you’ve ever found yourself pondering this question, you’re not alone. Understanding the voltage of a battery is essential for a multitude of everyday tasks, from powering your electronic devices to jump-starting a car. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of battery voltage and help demystify this often overlooked but crucial aspect of our daily lives. So whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply curious about how our modern world stays powered, join us as we dive into the world of volts and batteries. Let’s get started!
How Many Volts in a Battery?
Understanding Voltage in Batteries
Batteries are portable sources of electrical energy that power a wide range of devices, from cell phones and laptops to cars and power tools. One important characteristic of a battery is its voltage, which determines how much electrical potential energy it can provide. In simpler terms, voltage is the force that pushes electrons through a circuit, enabling the flow of electrical current.
Voltage is typically measured in volts (V) and is a fundamental unit in the field of electricity. It is essential to understand the voltage of a battery to ensure compatibility with the device it is intended to power.
Standard Voltage Ratings for Common Batteries
Different types of batteries have different voltage ratings. Let’s take a closer look at the standard voltage ratings for some common types of batteries:
- Alkaline Batteries: Alkaline batteries are widely used in household devices such as remote controls, flashlights, and toys. They have a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts (V) and are available in various sizes, including AA, AAA, C, and D.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries are known for their high energy density and long shelf life. They are commonly used in cameras, watches, and medical devices. Lithium batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3 volts (V). However, some variations can have higher voltages.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: NiMH batteries are rechargeable and are commonly used in portable electronics, such as digital cameras and cordless phones. They have a nominal voltage of 1.2 volts (V), slightly lower than alkaline batteries, but can provide consistent power output throughout their discharge cycle.
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries: Another type of rechargeable battery, NiCd batteries, have a nominal voltage of 1.2 volts (V), just like NiMH batteries. However, NiCd batteries have become less popular due to environmental concerns over the cadmium they contain.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in automotive applications, providing the necessary power to start the engine. These batteries have a nominal voltage of 12 volts (V) and consist of several cells connected in series to reach this voltage.
Voltage Variations and Load Conditions
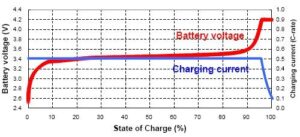
While batteries have standard nominal voltage ratings, it is important to note that the actual voltage can vary depending on certain factors. One of the key factors influencing battery voltage is the load placed on it.
When a device is connected to a battery, it creates an electrical load. As the load increases, the voltage output of the battery may decrease. This voltage drop occurs due to internal resistance within the battery and the energy consumed by the device. It is important to consider this voltage drop while selecting a battery for a specific device to ensure proper functionality.
Series and Parallel Battery Configurations
To increase the voltage output or provide higher capacity, batteries can be connected in series or parallel configurations.
- Series Configuration: When batteries are connected in series, the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next battery. This arrangement increases the total voltage while keeping the capacity constant. For example, two 1.5V batteries connected in series will provide a total voltage of 3V, while the capacity remains the same.
- Parallel Configuration: In a parallel configuration, the positive terminals of batteries are connected together, and the same is done for the negative terminals. This configuration increases the total capacity while maintaining the same voltage. For instance, two 1.5V batteries connected in parallel will still have a total voltage of 1.5V, but the capacity will be doubled.
It is crucial to understand the appropriate battery configuration required for a specific device to ensure compatibility and desired performance.
Understanding the voltage of a battery is essential when choosing the right power source for your devices. Different batteries have different voltage ratings, ranging from 1.2V to 12V, depending on the type and application. It is crucial to select a battery with the appropriate voltage to ensure compatibility and optimal functionality. Additionally, considering voltage variations under load conditions and the possibility of series or parallel battery configurations can help meet specific power requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many volts are typically found in a battery?
Most common batteries, such as AA or AAA batteries, have a voltage of 1.5 volts.
Are there batteries with higher voltages?
Yes, there are batteries available with higher voltages. For example, 9-volt batteries are commonly used in smoke alarms and some electronics.
What types of batteries have lower voltage?
Button cell batteries, commonly found in watches and small electronic devices, typically have a lower voltage ranging from 1.2 to 3 volts.
Can the voltage of a battery vary?
Yes, the voltage of a battery can vary depending on its chemistry and condition. Over time, as a battery depletes its energy, the voltage may decrease.
Can I combine multiple batteries to increase the voltage?
Yes, you can increase the voltage by connecting multiple batteries in series. For example, connecting two 1.5-volt batteries in series will result in a total voltage of 3 volts.
Why is it important to know the voltage of a battery?
Knowing the voltage of a battery is important because different devices and appliances require specific voltage levels to function properly. Using a battery with the wrong voltage can damage the device or prevent it from working correctly.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the voltage of a battery is crucial for various applications. The voltage measurement of a battery indicates the electrical potential difference between its terminals, which determines its overall power output. Most commonly, a household battery contains 1.5 volts, while car batteries have a higher voltage of around 12 volts. It is essential to consider the voltage requirement of your devices and appliances to ensure proper functioning and prevent damage. Overall, knowing how many volts are in a battery is essential for powering our everyday devices effectively.