Looking to charge your electric vehicle (EV) but unsure about the amperage needed for your charger? You’ve come to the right place! How many amps does an EV charger need? This burning question can cause confusion for many EV owners, but fear not. In this article, we will provide you with a clear and concise answer, equipping you with the knowledge to make the right decision for your charging needs. So, let’s dive in and demystify the amperage requirements for EV charging.
How Many Amps Does an EV Charger Need?
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular due to their eco-friendly nature and the lower cost of electricity compared to gasoline. If you own or plan to purchase an electric vehicle, one of the essential considerations is the type of charging equipment you will need. EV chargers come in various types, and understanding how many amps your charger requires is crucial for safe and efficient charging. In this article, we will delve into the world of EV chargers and explore the factors that determine how many amps an EV charger needs.
Understanding Amps and Charging Levels
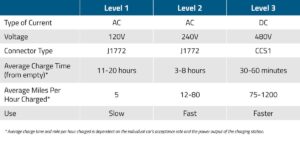
Before we dive into the specifics of EV charger amperage, let’s briefly understand amps and charging levels. Amps, short for amperes, refer to the electrical current flowing through a circuit. The charging level relates to the speed at which an electric vehicle charges. EV charging levels are standardized, and the three common levels are:
1. Level 1 Charging: This is the slowest charging method and typically relies on a standard 120-volt household outlet. Level 1 chargers usually provide around 1.4 to 1.9 kW of power, equivalent to approximately 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging.
2. Level 2 Charging: Level 2 chargers offer faster charging speeds than Level 1. They require a 240-volt electrical circuit and provide power ranging from 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW. Level 2 charging stations can deliver up to 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
3. Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging): DC fast chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers, are the fastest charging option commercially available. They use direct current (DC) to charge the vehicle’s battery rapidly. Level 3 chargers require specialized infrastructure and are mostly found in public charging stations. They can deliver around 60-80 miles of range in just 20 minutes of charging.
Factors Affecting Amps Required for an EV Charger
Several factors impact the number of amps an EV charger needs. Understanding these factors will help you determine the appropriate amperage for your specific charging needs.
- Vehicle Capability: Different electric vehicles have varying charging capabilities. Some vehicles may have built-in chargers that can handle higher amperages, while others may have limitations. It is crucial to check your vehicle’s specifications and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the recommended amperage.
- Charger Type: Different EV chargers have different amperage requirements. Level 1 chargers typically draw around 12-16 amps, while Level 2 chargers can range from 16 to 80 amps. DC fast chargers require even higher amperage, often exceeding 100 amps. It’s important to choose a charger that aligns with your vehicle’s and electrical system’s capabilities.
- Electrical Service: The electrical service in your home or facility plays a significant role in determining the amperage you can provide to your EV charger. Older homes may have electrical systems with lower amp capacities, while newer homes or commercial buildings typically have higher capacities. It’s important to assess your electrical service and consult an electrician if necessary to ensure it can support the desired amperage.
- Wiring and Circuit Breaker: The wiring and circuit breaker between your electrical panel and the EV charger must be rated to handle the chosen amperage. Thick enough wiring and an appropriately sized breaker are essential to prevent overheating and electrical hazards. Consulting an electrician is recommended to ensure proper wiring and breaker selection.
- Utility Connection: If you plan to install a high-amperage EV charger, you may need to contact your utility company to ensure they can provide the required electrical service. Some utility companies may require upgrades or additional fees for high-amperage connections.
Determining the Right Amperage for Your EV Charger
To determine the right amperage for your EV charger, you should consider the following steps:
- Check Your Vehicle’s Specifications: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the recommended charging amperage for your specific model.
- Evaluate Your Electrical System: Assess your electrical service to determine its amp capacity. This may involve contacting an electrician to inspect your electrical panel and wiring.
- Choose a Charging Level: Based on your vehicle’s capability and electrical system evaluation, decide on the charging level that suits your needs (Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3).
- Select an Appropriate Charger: Select an EV charger that aligns with your chosen charging level and amperage requirements. Ensure the charger is compatible with your vehicle and meets safety standards.
- Install the Charger: Work with a licensed electrician to install the charger correctly. They will ensure proper wiring, circuit breaker selection, and adherence to local electrical codes.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Amperage
Selecting the appropriate amperage for your EV charger offers several benefits:
- Efficient Charging: The right amperage ensures your electric vehicle charges at an optimal speed, minimizing charging time while maximizing range.
- Safety: Choosing the correct amperage helps prevent electrical overloads, minimizing fire hazards and electrical damage to your vehicle or property.
- Cost Savings: Higher amperage chargers allow for faster charging, potentially reducing the demand on peak electrical rates and saving money on your utility bill.
- Future Proofing: Installing an EV charger with higher amperage than your current vehicle requires can future-proof your charging setup. If you upgrade to a vehicle with higher charging capabilities in the future, you won’t need to replace the charger.
Determining how many amps an EV charger needs is a crucial step in ensuring safe and efficient charging for your electric vehicle. By considering factors such as your vehicle’s capabilities, charger type, electrical service, and wiring, you can select the appropriate amperage for your specific needs. Remember to consult your vehicle’s specifications, work with a licensed electrician, and choose a charger that aligns with your charging requirements. Making the right amperage choice will result in faster charging, improved safety, and enhanced convenience in your EV charging experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the required amperage for an EV charger?
The required amperage for an EV charger can vary depending on the specific model and the capacity of your electric vehicle. However, most residential EV chargers typically require a minimum of 40 amps to safely charge your electric vehicle.
Can I install an EV charger with a lower amp rating?
While it is technically possible to install an EV charger with a lower amp rating, it may not provide sufficient charging power for your electric vehicle. Charging at a lower amp rating will result in slower charging times and may not meet your vehicle’s charging needs. It is recommended to install an EV charger with the minimum amp rating recommended by the manufacturer.
What happens if I exceed the amp rating of my EV charger?
If you exceed the amp rating of your EV charger, it can cause the circuit breaker to trip, leading to a loss of power. Additionally, exceeding the amp rating can result in overheating of the charger and potential damage to the electrical system of your vehicle. It is important to ensure that your EV charger is correctly matched to the amp rating required by your vehicle.
Do commercial EV chargers require higher amperage than residential chargers?
Commercial EV chargers often require higher amperage compared to residential chargers. This is because commercial charging stations need to accommodate multiple vehicles charging simultaneously and provide faster charging speeds. Commercial EV chargers can range from 60 amps to as high as 400 amps, depending on the specific charging station and its intended usage.
Can I upgrade my electrical panel to support a higher amp charger?
Yes, it is possible to upgrade your electrical panel to support a higher amp charger. However, it is essential to consult with a licensed electrician to assess your current electrical system’s capacity and determine if an upgrade is feasible. Upgrading the electrical panel can ensure that your home or business can handle the increased power demand without overloading the system.
Final Thoughts
An EV charger requires a specific number of amps to function properly. The required amperage depends on the power rating of the charger and the charging speed desired. For residential charging stations, most electric vehicles need a 40-amp or 50-amp circuit, which provides enough power to charge at a reasonable speed. However, some high-powered chargers may require 60-amps or even higher. It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific EV charger being used to determine the necessary amperage. By understanding how many amps an EV charger needs, we can ensure efficient and safe charging for electric vehicles.