Looking to dive into the fascinating world of batteries? If you’ve ever wondered how many cells are in a 12-volt battery, you’ve come to the right place! Understanding the inner workings of batteries can be a bit perplexing, but fear not, because we’re here to guide you through it. So, let’s uncover the mystery together and discover the answer to the question, how many cells are in a 12-volt battery? Ready to explore the intricate pathways of electrical power? Let’s get started!
How Many Cells are in a 12 Volt Battery: Exploring the Basics
An Introduction to Cells and Batteries
When we talk about batteries, it’s important to understand the basic unit that powers them – the cell. A battery is essentially a collection of cells that work together to generate electrical energy. Each cell consists of two electrodes – a positive electrode (cathode) and a negative electrode (anode) – separated by an electrolyte. Cells can come in various sizes and voltages, depending on their intended purpose.
One common type of battery is the 12 volt battery, which is widely used in automobiles, boats, and other applications. But have you ever wondered how many cells are inside a 12 volt battery? In this article, we will dive deep into the topic and explore everything you need to know about the number of cells in a 12 volt battery.
Understanding the Voltage of a 12 Volt Battery
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s start by understanding the significance of the voltage rating of a battery. Voltage measures the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. In the case of a battery, it represents the amount of electrical force it can exert to move charges through a circuit.
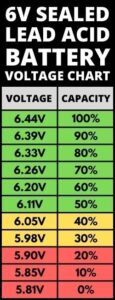
A 12 volt battery, as the name suggests, has a voltage rating of 12 volts. This voltage is achieved by combining multiple cells within the battery. Each individual cell typically has a voltage rating of 2.1 to 2.2 volts, depending on the chemistry and design. Therefore, a 12 volt battery comprises of six cells connected in series, with each cell providing approximately 2 volts of the total voltage.
The Role of Cells in a 12 Volt Battery
Now that we understand the voltage rating of a 12 volt battery, let’s explore the role of cells within it. Each cell in a 12 volt battery contributes a fraction of the overall voltage, and when these cells are connected in series, their voltages add up to produce the desired 12 volts.
In a 12 volt battery, the cells are typically connected in a series circuit, meaning the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell. This series connection allows the voltages to add up, resulting in a higher total voltage.
The Chemistry Behind 12 Volt Battery Cells
Different types of batteries use different chemical reactions to generate electricity. In the case of a 12 volt battery, there are several chemistries commonly used, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-cadmium. Let’s briefly explore the chemistry behind the most common type – the lead-acid battery.
Lead-acid batteries are widely used in automotive applications due to their robustness and affordability. Each cell in a lead-acid battery consists of a lead dioxide (PbO2) positive electrode, a lead (Pb) negative electrode, and a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) electrolyte. During discharge, the sulfuric acid undergoes chemical reactions with the electrodes, producing lead sulfate (PbSO4) and releasing electrons.
The Internal Structure of a 12 Volt Lead-Acid Battery
To better understand how cells are arranged in a 12 volt lead-acid battery, let’s take a closer look at its internal structure. A typical 12 volt lead-acid battery consists of six cells connected in series. Each cell is housed in its own compartment within the battery casing.
Inside each cell, there are lead plates immersed in sulfuric acid electrolyte. The positive electrode, made of lead dioxide, is connected to the positive terminal of the battery, while the negative electrode, made of lead, is connected to the negative terminal. These electrodes are separated by a permeable membrane or separator, which prevents direct contact but allows the movement of ions during the chemical reactions.
The Importance of Maintaining a 12 Volt Battery
Keeping your 12 volt battery in good condition is crucial for its longevity and performance. Here are a few tips to help you maintain your battery effectively:
- Regularly check the battery’s electrolyte levels and top up with distilled water if necessary.
- Keep the battery terminals clean and free from corrosion. Use a solution of baking soda and water to clean any residue.
- Avoid overcharging the battery, as it can lead to excessive heat and damage. Use a suitable charger that matches the battery’s voltage and chemistry.
- If your battery is not in use for an extended period, consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger to keep it charged and avoid sulfation.
- Ensure the battery is securely mounted in your vehicle or equipment to prevent vibrations that can damage the internal components.
In conclusion, a 12 volt battery comprises of six cells connected in series, with each cell providing approximately 2 volts of the total voltage. Understanding the basics of cells and their role in a 12 volt battery is essential for maintaining and maximizing the performance of your battery. Whether it’s a lead-acid, lithium-ion, or nickel-cadmium battery, the principles remain the same. By taking proper care of your battery, you can extend its lifespan and ensure reliable power for your applications. Remember to follow the recommended maintenance guidelines provided by the battery manufacturer and consult a professional if you have any concerns or issues with your battery.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many cells are there in a 12 volt battery?
A 12 volt battery typically consists of six cells.
Why does a 12 volt battery have multiple cells?
A 12 volt battery contains multiple cells to achieve the desired voltage. Each cell in the battery provides approximately 2.1 volts, and when connected in series, their voltages add up to reach the total voltage of 12 volts.
What is the purpose of having multiple cells in a 12 volt battery?
Having multiple cells allows for a higher voltage output, which is necessary to power devices that require 12 volts. It also increases the overall capacity and energy storage of the battery.
Can a 12 volt battery have a different number of cells?
While the standard configuration for a 12 volt battery is six cells, it is possible for manufacturers to use a different number of cells to achieve the desired voltage. However, this is less common and usually done for specific applications.
What happens if a cell in a 12 volt battery fails?
If a cell in a 12 volt battery fails, it can significantly impact the battery’s overall performance and lifespan. The battery may experience reduced voltage output, decreased capacity, or complete failure. In such cases, it is recommended to replace the battery to ensure optimal performance.
Are all 12 volt batteries the same in terms of cell configuration?
No, the cell configuration of a 12 volt battery can vary depending on the specific battery type, design, and manufacturer. It is essential to check the specifications of a particular battery to determine the number of cells it contains.
Final Thoughts
A 12-volt battery is typically composed of six individual cells. Each cell produces about 2 volts of power, which when combined in series, adds up to the 12 volts required for the battery. These cells are usually made of lead plates submerged in sulfuric acid electrolyte. By maintaining each cell in good condition and monitoring their voltage levels, one can ensure the battery’s overall performance and longevity. Understanding the number of cells in a 12-volt battery is important for handling, maintenance, and troubleshooting purposes.